
Mom and Baby Care
Product benefits
We are here for your every motherhood journey – as early as 13 weeks of pregnancy.
If you’re an expecting parent, our Mom and Baby Care prenatal plan is comprehensive insurance for pregnant mothers that can help to protect the health and financial needs for both mother and baby altogether, should any complication arise.
ELITE PLAN
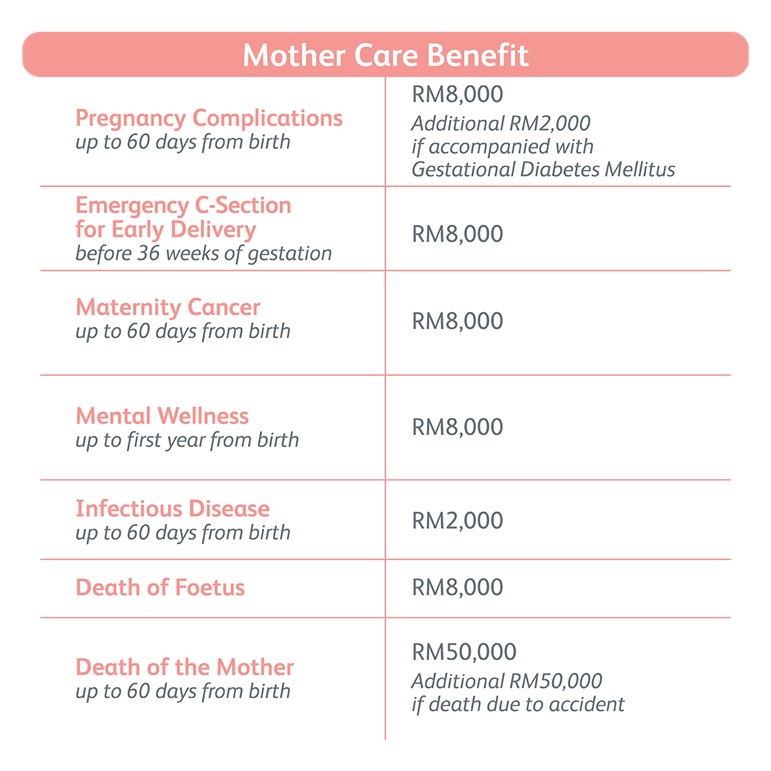
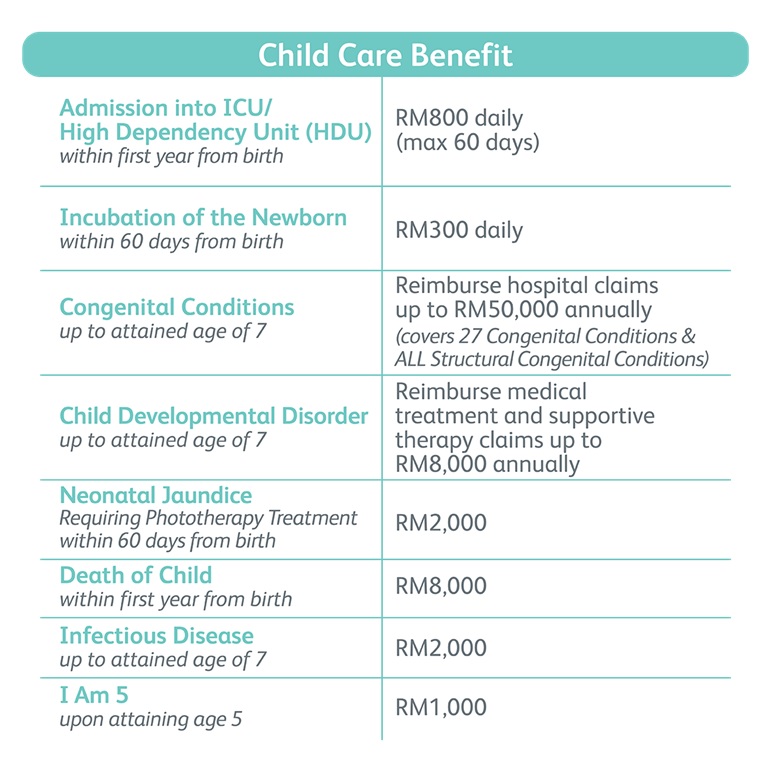
There are 2 other plans available for Mom and Baby Care. Please speak to Prudential Wealth Planner for more info.
You may also want to explore our comprehensive solution that covers both pregnancy insurance and continuous coverage for your child, PRUMy Child Plus.
Attachable plan

The basic plan that Mom and Baby Care can be attached to:
Learn more
Cost of Insurance Rates
Important notes
This content contains only a brief description of the product and is not exhaustive. You are advised to refer to Prudential Assurance Malaysia Berhad (PAMB)’s Brochure, Product Disclosure Sheet, Product / Sales Illustration, Fund Fact Sheet (if any), before purchasing the plan, and to refer to the terms and conditions in the policy document for details of the features and benefits, exclusions and waiting periods under the policy.
PROTECTION BY PERBADANAN INSURANS DEPOSIT MALAYSIA (“PIDM”) ON BENEFITS PAYABLE FROM THE UNIT PORTION OF THIS CERTIFICATE/POLICY IS(ARE) SUBJECT TO LIMITATIONS. Please refer to PIDM’s Takaful and Insurance Benefits Protection System (“TIPS”) Brochure or contact Prudential Assurance Malaysia Berhad or PIDM (visit www.pidm.gov.my).
FAQ
When does an emergency C-section before 36 weeks become necessary?
An emergency C-section delivery may be necessary if there are complications that threaten the health and safety of the mother and/or baby, such as:
- Preterm labour (labour before 36 weeks of pregnancy)
- Placenta previa or placental abruption (placenta covering the cervix or separating from the uterine wall, respectively)
- Foetal distress (baby showing signs of lack of oxygen or distress)
- Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) (baby not growing at a normal rate)
- Pre-Eclampsia (serious pregnancy complication characterised by high blood pressure and organ damage)
These decisions are made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account the specific circumstances of each pregnancy.
What are Structural Congenital Conditions?
*Structural Congenital Conditions are birth defects that affect the normal physical development of body parts or organs.
Examples include but not limited to:
-
Cleft Lip
-
Abnormal limbs (e.g. Clubfoot);
-
Heart defects (e.g. Atrial/Ventricular Septal Defects, Patent Ductus Arteriosus);
-
Gastrointestinal defect (e.g. Esophageal Atresia, Diaphragmatic Hernia, Pyloric Stenosis).
We do not cover functional birth defects (other than listed Congenital Conditions) which are related to a problem with how body system works.
Examples include but not limited to:
-
Nervous system and brain problems (e.g. learning disabilities, intellectual impairment, behavioral disorders);
-
Immune system disorders in which the child’s immune system does not function adequately (e.g. autoimmune diseases);
-
Neurodevelopmental disorders where the child seems to be developing normally but suddenly starts to lose function and previously acquired skills (e.g. Rett Syndrome, Muscular Dystrophy);
-
Metabolic disorders (e.g. Phenylketonuria, Type 1 Diabetes).
What are child developmental disorders?
Child developmental disorders are conditions that arise from cognitive and/or physical impairments. They are usually identified in childhood and are likely to last throughout the individual’s lifetime.
What are common child developmental disorders?
Some common child developmental disorders include
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
- Down syndrome.
- Cerebral palsy.
- Language and learning disorders.
- Vision and hearing impairment.
Is emergency caesarean very painful?
Aside from the pain you might feel from labour and/or conditions leading up to the emergency c-sec, the c-section surgery itself is painless. A regional anesthesia will be given, and you’ll be numb waist down. You may, however, feel a pulling or pressure sensation.
What are the main causes of jaundice?
Infant jaundice, or neonatal jaundice, is caused by excess bilirubin, a pigment released during the breakdown of old or ‘used’ red blood cells. Newborn babies produce more bilirubin because of higher production and breakdown of red blood cells during their first few days of life. Additionally, a newborn’s liver is sometimes not developed enough to remove bilirubin quickly, resulting in excessive bilirubin.
Does jaundice go away?
Mild jaundice usually goes away and resolves on its own as your newborn begins to feed. However, treatment might be needed if your baby has jaundice for longer than 2 weeks.
Will insurance pay for my baby’s jaundice treatment?
This depends on your insurance policy. For example, Prudential’s Mom and Baby Care plan covers phototherapy treatment for neonatal jaundice within 60 days from birth.
Why are newborn babies put in incubator?
Incubation for newborn preterm babies is needed because preemies do not have enough body fat to hold their own body temperature. Incubators are small beds enclosed in clear hard plastic. The temperature in the incubator can be controlled to ensure that the preemie’s body temperature is where it should be.
How long does a baby stay in an incubator?
Premature babies usually go to the NICU (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit) within hours of birth. How long they stay in an incubator depends very much on their health condition and how many weeks gestation they are born at. As such, some babies are incubated for a few days while others a few weeks or even months.
Is Prudential’s Mom and Baby Care plan a type of pregnancy insurance?
Yes, Prudential’s Mom and Baby Care is maternity insurance that covers both mother and child from 13 weeks of pregnancy up till the child is 7 years old. Benefits for the mother include pregnancy complications, emergency c-section delivery, maternity cancer, mental wellness, and infectious disease. Benefits for the baby include admission into ICU/HDU, incubation of the newborn, congenital conditions, child developmental disorder, and neonatal jaundice.




